This page includes explanations of some of the terms and phrases that you may come across in relation to web sites.
ADSL – Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
A DSL line where the upload speed is different from the download speed. Usually the download speed is much greater.Sometimes referred to as broadband, although broadband simply refers to the ‘bandwidth’ not the type of transmission system.
ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange
A world-wide standard for the code numbers used by computers to represent all the upper and lower-case Latin letters, numbers, punctuation, etc. There are 128 standard ASCII codes each of which can be represented by a 7 digit binary number: 0000000 through 1111111.
BReturn to alphabetical INDEX
Bandwidth
How much data you can send through a connection at any one time. Usually measured in bits-per-second (bps.) A full page of English text is about 16,000 bits. A fast modem can move about 57,000 bits in one second. Full-motion full-screen video would require roughly 10,000,000 bits-per-second, depending on compression.
Blog – weB LOG
A blog is a journal that is available on the web. The activity of updating a blog is “blogging” and someone who keeps a blog is a “blogger.” Blogs are typically updated daily using software that allows people with little or no technical background to update and maintain the blog. One of the most popular is WORDPRESS which is open source and written in the language PHP.
Body
HTML pages are normally split into HEAD and BODY. The head contains a range of tags and code that will be used by the browser to create the page, but will not be visible to the user. The Body contains all of the information that will be shown to the user.
bps – bits-per-second
A measurement of how fast data is moved from one place to another. A 56K modem can move about 57,000 bits per second. There are 8 bits to a byte which is the basic requirement for a number or character using conventional ASCII.
Browser
A Client program (software) that is used to communicate with web servers. The most common is Internet Explorer, but a range of others are available, including Mozilla Firefox, Safari and Google Chrome.
Byte
A set of bits that represent a single character. Normally there are 8 bits in a byte, which leads to larger numbers kilobyte (1000 or 1024 bytes), gigabytes (1000 or 1024 kilobytes).
CReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page CAT5e
Standard for ethernet cables that allow a rate of data transfer between routers of 100 megabytes. Now superceded by CAT6 which is guaranteed for Gigabyte transfer speeds.
Certificate Authority
An issuer of Security Certificates used in SSL (Secure Socket Layer) or encrypted connections.
CGI – Common Gateway Interface
A set of rules that describe how a Web Server communicates with another piece of software on the same machine. Any piece of software can be a CGI program if it handles input and output according to the CGI standard.
cgi-bin
The traditional name of a directory on a web server in which CGI programs are stored.
Client
A software program that is used to contact and obtain data from a Server software program on another computer. For example, a Web Browser is a specific kind of Client.
Cookie
This refers to a piece of information sent by a Web Server to a Web Browser that the Browser software is expected to save and to send back to the Server whenever the browser makes additional requests from the Server.
CSS – Cascading Style Sheet
A standard for specifying the appearance of text and other elements in an html page. CSS is used to provide a single reference library of styles that are used over and over throughout a large number of related documents on a web site. Anything specified in a CSS file will appear in all pages referenced to the file, simplifying overall style changes.
Cyberspace
Term originated by author William Gibson in his novel Neuromancer, normally used to describe the whole range of resources on the internet.
DReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Dedicated Server
A hosting service where one web site is maintained on a single dedicated computer.
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DHCP is a protocol by which a machine can obtain an Internet Protocol (IP) number and network configuration information from a server on the local network.
DHTML – Dynamic HyperText Markup Language
DHTML refers to web pages that use a combination of HTML, JavaScript, and CSS to create features such as simple kinds of animation, and many more.
DNS – Domain Name System
The Domain Name System is the system that translates Internet domain names that users can understand into IP numbers that can be sued to locate the server where the site is located. A DNS Server is a server that performs this kind of translation.
Domain Name
The unique name that identifies an Internet site.
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line
A method for moving data over copper telephone lines. A DSL circuit is faster than a regular phone connection, using a digital process to transfer data. If the speed of the upstream and the downstream is different it is called ADSL (Asynchronous DSL). In theory ADSL allows download speeds of up to 9 megabits per second and upload speeds of up to 640 kilobits per second, but this will depend on distance to the exchange.
EReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
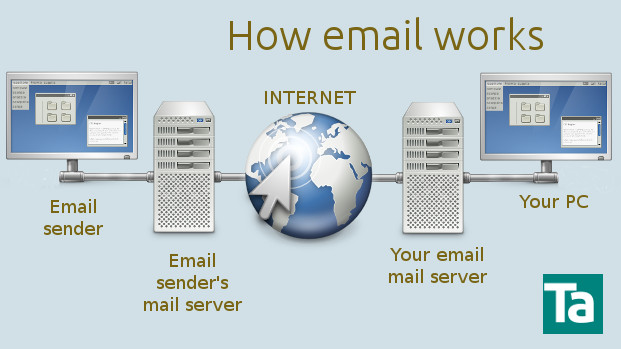
Email – Electronic Mail
Electronic messages, sent from one person to another via computer. E-mail can also be sent automatically to a large number of addresses. Originally, text only it is now common for attachments and html elements, although this has security implications.
Ethernet
A very common method of networking computers in a Local Area Network or LAN. The common standard is 100-BaseT”which can handle up to about 100,000,000 bits-per-second and can be used with almost any kind of computer.
Extranet
An intranet that is accesible to computers that are not physically part of a companys’ own private network, but that is not accessible to the general public, for example to allow vendors and business partners to access a company web site.
FReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
FDDI – Fibre Distributed Data Interface
A standard for transmitting data on optical fibre cables at a rate of around 100,000,000 bits-per-second (10 times as fast as 10-BaseT Ethernet).
Fire Wall
A combination of hardware and software that separates a Network into two or more parts for security purposes. Often used to isolate the LAN from the wider network, commonly referred to as WAN.
Flame
In the context of online debates in forums or on blogs, to ‘flame’ someone refers to any kind of derogatory comment no matter how witless or crude and the debate degenerates into a series of personal attacks.
FTP – File Transfer Protocol
A common method of moving files between two Internet sites or servers. It is most commonly used for transferring html files to the server itself, for updating the content of web sites, although many web sites that have files for downloading will use the ftp protocol.
GReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Gateway
The technical meaning is a hardware or software set-up that translates between two dissimilar protocols.
GIF – Graphic Interchange Format
Generally web site image files are in one of 3 formats – GIF, JPEG and increasingly PNG as they are best suited to compression which conserves bandwidth. The GIF format is especially suitable for images containing large areas of the same color, for example logos, icons and shading. In addition they can have transparent backgrounds – not possible with jpegs. GIF format files of simple images are usually smaller than the same file would be if stored in JPEG format, but GIF format does not store photographic images as well as JPEG.
Gigabyte
1000 or 1024 megabytes. The 1000 or 1024 causes great controversy amongst the IT fraternity!
GZIP Compression
A compression standard often used on web servers to compress files that are served to the browser. Most modern browsers support this standard and decompress the files when they receive them. It reduces bandwidth considerably, but increases the cpu load at either end.
HReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Hit
As used in reference to the World Wide Web, hit means a single request from a web browser for a single item from a web server; thus in order for a web browser to display a simple page that contains 5 graphics, 6 hits occur at the server: 1 for the HTML page, and one for each of the 5 graphics. The number of associated items is a major factor in download speed as the more items the longer download will take – a significant issue if the user is connected via modem.
Head
HTML pages are normally split into HEAD and BODY. The head contains a range of tags and code that will be used by the browser to create the page, but will not be visible to the user. The Body contains all of the information that will be shown to the user.
Home Page
Originally, the web page that your browser is set to use when it starts up. It is also used to refer to the main ‘index’ page of a web site which is the default Home Page for the site. So, if you do not give the page address the browser will look for any page that is called index.xxx. The xxx is normally html or htm but could also be php if the site is using this language.
Host
Any computer on a network that runs services available to other computers on the network. A server is pefectly able to provide a range of services, such as SMTP (email) and HTTP (web).
Hosting
The term used to describe the process of storing a web site. Hosting companies provide banks of computers that are used to host a number of web sites. A range of offers include Shared Hosting, where one computer deals with multiple site through to Dedicated Servers which host only one web site.
HTML – HyperText Markup Language
The coding language used to create documents for use on the World Wide Web. HTML looks like typesetting code (also call type markup), where you surround a block of text with codes that indicate how it should appear.The “hyper” means you can link page elements to another file on the server or wider internet. Any text editor can read a html file, but the files are viewed using a “Web Browser” which interprets the markup to display the page.If you want to see the code of any web page you can use your browsers ‘VIEW SOURCE’ facility which will show the marked up text. HTML is expected to eventually be replaced by XML-based XHTML standards.
HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol
The protocol for moving hypertext files across the Internet. Requires a HTTP client program on one end, and an HTTP server program (such as Apache) on the other. HTTP is the most important protocol used in the World Wide Web (WWW).
Hypertext
Any text that contains links to other documents – words or phrases in the document that can be chosen by a reader and which cause another document to be retrieved.
IReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol
IMAP is gradually replacing simpler POP as the main protocol used by email clients in communicating with email server. An email client program can also manipulate message stored on the server, without retrieving the messages. So messages can be deleted, have their status changed, multiple mail boxes can be managed, etc.
Internet
The inter-connected networks that are connected using the TCP/IP protocols across tens of thousands of independent networks into the global internet.
Intranet
A private network inside an organization that uses the same kinds of software that you would find on the public Internet, but that is only for internal use. Compare with extranet.
IP Number – Internet Protocol Number
A unique number consisting of 4 parts separated by dots. Every machine that is on the Internet has a unique IP number. Many servers also have one or more Domain Names as a domain name can share IP numbers.The most widely used version of the Internet Protocol (the “IP” part of TCP/IP.) IPv4 allows for a theoretical maximum of approximately four billion IP Numbers, but the actual number is far less due to inefficiencies in the way blocks of numbers are handled by networks and the rapid increase in new web sites. The gradual adoption of IPv6 successor to IPv4 and provides a huge number of available IP Numbers – over sextillion addresses. IPv6 allows every device on the planet to have its own IP Number.
IRC – Internet Relay Chat
Multi-user live chat facility. There are a number of major IRC servers around the world which are linked to each other. Anyone can create a channel and anything that anyone types in a given channel is seen by all others in the channel. Private channels can be created for multi-person conference calls.
ISDN – Integrated Services Digital Network
A system to transfer data over existing regular phone lines. It can provide speeds of roughly 128,000 bits-per-second over telephone lines. Unlike DSL, ISDN can be used to connect to many different locations, one at a time, just like a regular telephone call, as long the other location also has ISDN.
ISP – Internet Service Provider
An institution that provides access to the Internet.
JReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Java
Java is a network-friendly programming language invented by Sun Microsystems, used for a range of projects including transaction processing systems as well as editors, audio players, web browsers as well as for creating programs that run in small electronic devices, such as mobile telephones.Using small Java programs or Applets, Web pages can include functions such as animations, calculators, and other animated features.
JavaScript
JavaScript is a programming language mostly used in web pages, usually to add features that make the web page more interactive. When JavaScript is included in an HTML file it relies upon the browser to interpret the JavaScript.
JPEG – Joint Photographic Experts Group
One of the 3 image file formats used in web pages, JPEG format is preferred to the GIF format for photographic images as opposed to line art or simple logo art or colour gradients.
KReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Kilobyte
A thousand bytes, or 1024 bytes.
LReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page LAN – Local Area Network
A computer network limited to a local site. The current ethernet standards are limited to a range of 100m without repeated propogation which limits the area of the LAN – usually the same building.
Linux
A widely used Open Source operating system based on UNIX. Linux was first released by its inventor Linus Torvalds in 1991. In various forms it is the OS used on the majority of web servers across the world, providing the basis for the internet.
Login
The account name used to gain access to a computer system, or the act of connecting to a computer system by giving your credentials (usually your “username” and “password”)
MReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Megabyte
A million bytes. 1000 or 1024 kilobytes.
Meta Tag
A type of HTML tag that contains information not normally displayed to the user. Meta tags are normally in the HEAD section of the html page, and contains information about the page itself. From “meta” or “about this subject”Typical uses of Meta tags are to include information for search engines to help them better categorize a page and you can use your browser’s VIEW SOURCE feature to see them.
MIME – Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions
A standard for defining the types of files attached to standard Internet mail messages. The MIME standard is used where one computer programs needs to communicate with another program about what kind of file is being sent. For example, HTML files have a MIME-type of text/html, JPEG files are image/jpeg.
Mirror
The most common use of the term on the Internet refers to “mirror sites” which are web or FTP sites that maintain copies of material originated at another location, in order to provide more widespread access to the resource and spread the bandwidth and server load.
Modem – MOdulator, DEModulator
A device that connects a computer to a phone line. The maximum practical bandwidth using a modem over telephone lines is currently around 57,000 bps.
Mosaic
The first WWW browser that was available for the Macintosh, Windows,and UNIX all with the same interface. Mosaic started the popularity of the Web. The first version was released in late 1993.
NReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Network
Connect 2 or more computers together so that they can share resources and you have a computer network. Connect 2 or more networks together and you have an internet.
NIC – Network Information Center
Generally, any office that handles information for a network. An early example InterNIC, which was where most new domain names were registered in the early days of the internet. NIC-handle is a username given to hosting company customers. Also Network Interface card, used to link a computer to a network.
NNTP – Network News Transport Protocol
The protocol used by client and server software to carry USENET postings back and forth over a TCP/IP network. If you are using any of the more common software such as Netscape, Nuntius, Internet Explorer, etc. to participate in newsgroups then you are benefiting from an NNTP connection.
Node
Any single computer connected to a network.
OReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Open Content
Copyrighted information that is made available by the copyright owner to the general public under license terms that allow reuse of the material.
Open Source Software
Open Source Software is software for which the underlying programming code is available to the users so that they may read it, make changes to it, and build new versions of the software incorporating their changes.
PReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Packet Switching
The method used to move data around on the Internet. In packet switching, all the data coming out of a machine is broken up into small packets, each packet has the address of where it came from and where it is going. This enables packets of data from many different sources to co-mingle on the same lines, and be sorted and directed along different routes. This allows efficient use of the bandwidth available.
Password
A code used to gain access (login) to a locked system. Good passwords contain letters, both upper and lower case, non-letters and numbers.
PDF – Portable Document Format
A file format created to enable printing and viewing of documents to be the same regardless of computer operating system. Readers are available freely for all operating systems and you can also obtain programs that create PDF files of your own. The PDF format is based on the Postcript document-description language used in printing. Both PDF and Postscript were developed by the Adobe Corporation.
Perl – Practical Extraction and Report Language
Perl is a programming language that is widely used for both very simple, small tasks and for very large complex applications. During the 1990s it became the standard for creating CGI programs.
Permalink
A “permanent link” to a particular posting in a blog. A permalink is a URI that points to a specific blog posting, rather than to a web page in which the posting originally occured as it may be moved by the blogging software.
PHP – PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor
PHP is a programming language used for creating software that is part of a web site. The PHP language is designed to provide processing power on the web pages and particularly deal with databases like MySQL. PHP code is read and processed by the web server, whereas HTML is read and processed by the web browser.
Ping
To check if a server is running you can ‘ping’ it with a simple software routine – the response time can be used to measure the responsiveness of the server. Reputedly from the sound that a sonar locator system makes.
Plug-in
A piece of software that adds features to a larger piece of software.
PNG – Portable Network Graphics
PNG is a graphics format specifically designed for use on the World Wide Web. PNG enable compression of images without any loss of quality, including high-resolution images. The native format of Macromedia Fireworks graphics package.
Podcasting
A form of audio broadcasting using the Internet, podcasting takes its name from “iPod” and broad”casting”. Podcasting involves making one or more audio files available as “enclosures” in an RSS feed. A pod-caster creates a list of music or radio sound files and makes it available in the RSS 2.0 format. Others can get the list using various podcast “retriever” software which read the feed and then they can play the audio files at any time.
POP – Point of Presence, also Post Office Protocol
A Point of Presence usually means a city or location where a network can be connected to, often with dial up phone lines. Post Office Protocol refers to a way that e-mail client software such as Outlook Express gets mail from a mail server. When you obtain an account from an Internet Service Provider (ISP) you almost always get a POP account with it, and it is this POP account that you tell your e-mail software to use to get your mail.
Port
A place where information goes into or out of a computer, or both. On the Internet port often refers to a number that is part of a URL, appearing after a colon (:) right after the domain name. Every service on an Internet server listens on a particular port number on that server. Most services have standard port numbers, e.g. Web servers normally listen on port 80. Services can also listen on non-standard ports, in which case the port number must be specified in a URL when accessing the server.
Portal
Usually used as a marketing term to describe a Web site that is or is intended to be the first place people see when using the Web. Typically a “Portal site” has a catalog of web sites, a search engine, or both. A Portal site may also offer email and other service to entice people to use that site as their main “point of entry” (hence “portal”) to the Web.
PPP – Point to Point Protocol
The most common protocol used to connect home computers to the Internet via TCP/IP connections.
Protocol
A set of rules that define an exact format for communication between systems. The HTTP protocol defines the format for communication between web browsers and web servers and the SSL protocol defines a format for encrypted communications over the Internet. Normally defined in RFC documents.
Proxy Server
A Proxy Server sits in between a Client and the “real” Server that a Client is trying to use. Client’s are sometimes configured to use a Proxy Server, usually an HTTP server. The clients makes all of it’s requests from the Proxy Server, which then makes requests from the “real” server and passes the result back to the Client. Sometimes the Proxy server will store the results and give a stored result instead of making a new one (to reduce use of a Network). Can also be used to surf the internet anonymously.
QReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page RReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Router
A special-purpose computer (or software package) that handles the connection between 2 or more Packet-Switched networks. Routers spend all their time looking at the source and destination addresses of the packets passing through them and deciding which route to send them on.
RSS – Real Simple Syndication
A commonly used protocol for syndication and sharing of content, originally developed to facilitate the syndication of news articles, now widely used to share the contents of blogs are often made using RSS feeds.
RSS is an XML-based summary of a web site, usually used for syndication and other kinds of content-sharing.There are RSS “feeds” which are sources of RSS information about web sites, and RSS “readers” which read RSS feeds and display their content to users.
SReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Search Engine
A system for searching the information available on the Web. Some search engines work by automatically searching the contents of other systems and creating a database of the results. Other search engines contains only material manually approved for inclusion in a database, and some combine the two approaches.
Security Certificate
A piece of information (often stored as a text file) that is used by the SSL protocol to establish a secure connection.
SEO – Search Engine Optimization
The practice of designing web pages so that they rank as high as possible in search results from search engines. This involves ensuring a web page clearly describe its subject, making sure it contains truly useful information, including accurate information in Meta tags, and arranging for other web sites to make links to the page.
Server
A computer, or a software package, that provides a specific kind of service to client software running on other computers. In relation to the internet these are usually email or web servers. The term can refer to a particular piece of software, or to the machine on which the software is running. A single web server machine can (and often does) have several different server software packages running on it, web site, email, database and PHP, for example – LAMP server.
Servlet
A small computer program designed to be add capabilities to a larger piece of server software. Common examples are “Java servlets”, which are small programs written in the Java language and which are added to a web server.
SGML – Standard Generalized Markup Language
Developed in 1986 SGML provides a rich set of rules for defining new data formats. XML is based on SGML. SGML is an International Standards Organization (ISO) standard: ISO 8879:1986.
SMTP — (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
The main protocol used to send electronic mail from server to server on the Internet. SMTP is defined in RFC 821 and modified by many later RFC’s.
SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol
A set of standards for communication with devices connected to a TCP/IP network. Examples of these devices include routers, hubs, and switches. SNMP is defined in RFC 1089
Spam (or Spamming)
Unwanted email messages, often sent in large numbers. It can often be relayed through servers that have nothing to do with the sender, or using innocent account holders email account details. The most insidious spam will include a virus or spyware programs which will be used against the recipient.
Spyware
Software that is secretly installed on a users computer often as part of another program and monitors use of the computer in some way without the users’ knowledge or consent. Most spyware tries to get the user to view advertising and/or particular web pages. Some spyware sends information about the user to its creator.
SQL – Structured Query Language
A specialized language for sending queries to databases. The most common is MySQL which runs on many web sites in conjunction with PHP.
SSL – Secure Socket Layer
A protocol designed by Netscape Communications to enable encrypted, authenticated communications across the Internet.
TReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Tag
A tag is a basic element of the languages used to create web pages (HTML) and similar languages such as XML. To tag also means to assign a keyword to a post on a blog or other items on a web site, which enables searches based on these keywords.
TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
This is the suite of protocols that defines the Internet. Originally designed for the UNIX operating system, TCP/IP software is now included with every major kind of computer operating system.
Telnet
The command and program used to login from one Internet siteto another. The telnet command/program gets you to the login: prompt of another host.
Terabyte
1000 or 1024 gigabytes.
TLD – Top Level Domain
The last (right-hand) part of a complete Domain Name. For example in the domain name www.moulindelusseau.com “.com” is the Top Level Domain. There are an increasing number of TLD’s, for example .com, .edu, .gov, .info, .net, .org, and a collection of two-letter TLD’s corresponding to the standard two-letter country codes, for example, .us, .fr, as well as specific variants like .co.uk, ac.uk. The idea was for each one to reflect the nature of the web site, for example .net was for internet based organizations, but inevitably the edges have become blurred for the non official sites.
Trojan Horse (or Trojan)
A computer program that is hidden inside another program or that masquerades as something else in order to trick potential users into running it. For example a game or image file. The term “Trojan Horse” comes from a ruse of war used by the Greeks in the siege of Troy. A Trojan computer program may spread itself by sending copies of itself from the host computer to other computers, it may have a destructive or information gathering purpose.
UReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Unix
A computer operating system (the basic software running on a computer, underneath things like word processors and spreadsheets). Unix is designed to be used by many people at the same time (it is multi-user) and has TCP/IP built-in. It is the most common operating system for servers on the Internet. Apple computers’ Macintosh operating system, as of version 10 (“Mac OS X”), is based on Unix.
URI – Uniform Resource Identifier
An address for a resource available on the Internet.The first part of a URI is called the “scheme”. the most well known scheme is http, but there are many others. Each URI scheme has its own format for how a URI should appear. An example of URIs using the http scheme: http://www.moulindelusseau.com/index.html. The term URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is synonymous with URI. URI has replaced URL in technical specifications.
VReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page Virus
Computer programming code that makes copies of itself without any concious human intervention. Some viruses might display messages, install other software or files, delete software or files. A virus requires the presence of some other program to replicate itself. Typically viruses spread by attaching themselves to programs and in some cases files, for example the file formats for Microsoft Word and Excel allow the inclusion of executable programs called “macros” which can be formed from a virus.
VOIP – Voice Over IP
A specification and various technologies used to allow making telephone calls over IP networks, often the Internet. VOIP technology allows users to talk over Internet connections. Costs for VOIP calls can be a lot lower as the nature of the IP networks allows for more efficient use of network resources.
VPN – Virtual Private Network
A network in which some of the parts are connected using the public Internet, but the data sent across the Internet is encrypted, so the entire network is “virtually” private.
VPS – Virtual Private Server
A type of hosting that emulates a dedicated or private web server. Using a system like XEN the PC that hosts the server is split into mini servers that run independently of each other. Depending upon the configuration the hosting company can set the resources available to each VPS. A cost effective alternative to a dedicated server for users who want more control of their system – and the skills to manage them.
WReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
WAN – Wide Area Network
Any internet or network that covers an area larger than a single building or LAN coverage range.
Web Page
A document designed for viewing in a web browser. Normally written in HTML, it can be generated using other software and files stored on the web server, for example PHP. A website is made of one or more web pages.
Website
All of the web pages and related files (images, CSS, scripts) that are accessible via the internet of www. Normally all the of pages in a web site share the same basic URL, but international organizations websites might cover a range of servers and domain names.
Wi-Fi – Wireless Fidelity
A form of wireless data communication, in relation to the internet Wi-Fi is Wireless Ethernet and the protocols allow a wireless connection (often encrypted) to a network via a wireless router, rather than using cables.
Wiki
A wiki is a web site for which allows for multi person authoring where the content can be easily edited and altered from the web browser in which you are viewing it. Typically there is an “edit” button on each page and the wiki is configured to allow either anyone or only people with passwords to edit each page. The word “wiki” comes from a Hawaiian word meaning “quick”. There are various versions but perhaps the best know in Mediawiki which is the format used by Wikipaedia.
Worm
A worm is a virus that does not infect other programs. It makes copies of itself, and infects additional computers (typically by making use of network connections) but does not attach itself to additional programs; however a worm might alter, install, or destroy files and programs.
WWW – World Wide Web
World Wide Web (or Web for short) is a term frequently used when referring to “The Internet”, WWW can be best described meanings as the universe of hypertext servers (HTTP servers), more commonly called “web servers”, which are the servers that serve web pages to web browsers.
XReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
XHTML – eXtensible HyperText Markup Language
HTML expressed as valid XML. XHTML is intended to be used where you would use HTML but is much more strictly defined, which has benefits in coding and writing for it as well as browser development. It is anticipated that XHTML will replace HTML. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a widely used system for defining data formats. XML provides a system to define complex data structures. From these definitions (or schema) a programmer can create a programs to reliably process data.
XMLRPC – XML Remote Procedure Call
A protocol for client-server communication that sends and receives information “on top of” HTTP. The data sent and received is in a particular XML format specifically designed for use with XMLRPC.
YReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page ZReturn to alphabetical INDEX at top of page
Top